The epidemiology of surgical induced AKI is currently unknown. However, recent reports on incidences of AKI indicate that every second surgical patient is affected by this complication. Since AKI is independently associated with adverse outcomes, an exact knowledge of the occurrence is imperatively needed to enhance the awareness for this critical condition, consequently optimize patient management in order to improve patient outcome. Moreover, it has a high impact on health policy and the results are urgently needed for designing new pre-emptive and therapeutic trials, which is the main goal of the RAPNetwork (Renoprotective Network) supported by the European Society of Anesthesiology (Initiator: Univ.-Prof. Dr. med. Alexander Zarbock).

Rationale
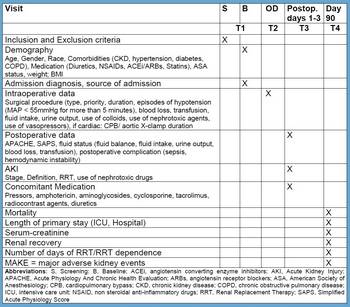
Study design
EPIS-AKI is an international multi-center, prospective observational study with the aim to include 10,000 patients to clarify the incidence and circumstances of the occurrence of acute kidney injury in patients undergoing major surgery.
The study is also registered at ClinicalTrials.gov.
Inclusion criteria
- Age ≥ 18 years
- Major operations with a duration of at least two hours
- Planned or unplanned admission to the ICU, IMCU or similiar after surgery
- Written informed consent
Exclusion criteria
- Pre-existing AKI
- AKI within the last three months
- End-stage renal disease with dialysis dependency
- Kidney transplant
Endpoints
Primary Endpoints
- The occurrence of AKI within 72h after surgery according to the KDIGO criteria
Secondary Endpoints
- Effect of preoperative risk factors on the incidence of postoperative AKI
- Effect of predetermined intraoperative factors on the impact of postoperative AKI
- Biomarkers of AKI (urine for this endpoint will be collected in some centres)
- Outcomes:
- Use of renal replacement therapy
- Length of ICU stay
- Length of hospital stay
- Survival
- ICU mortality
- Hospital mortality
- MAKE90 (major adverse kidney events at day 90): combined endpoint consisting of:
- Mortality
- Renal replacement therapy
- Persistent renal dysfunction defined as serum-creatinine ≥ 1.5 times as compared to baseline serum-creatinine
Steering Committee
- Alexander Zarbock
Department of Anesthesiology, Intensive Care and Pain Medicine
University Hospital Münster, Münster
Germany
- Thomas Rimmelé
Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care Medicine
Edouard Herriot Hospital, Lyon
France
- Max Bell
Department of Perioperative Medicine and Intensive Care
Karolinska University Hospital, Stockholm
Sweden
- Nandor Marczin
Section of Anaesthesia, Pain Medicine and Intensive Care
Imperial College, London
United Kingdom
- Stefano Romagnoli
Department of Anesthesia and Intensive Care
University of Florence, Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria Careggi, Florence
Italy
- Idit Matot
Division of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care and Pain Medicine
Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv
Israel
Current number of registered patients
10.000
in 28 participating countries
Patient registration competed. Now data completition.
CONTACT
Bureau of Clinical Investigations
Department for Anesthesiology,
Intensive Care and Pain Medicine
University Hospital Münster
Albert-Schweitzer-Campus 1
Complex A1
48149 Münster - Germany
T: + 49 251 83-47282
F: + 49 251 83-40501
epis-aki(at)ukmuenster(dot)de
epis-aki.ukmuenster.de